
It's critical to have systems in place to recognise and categorise new species, which are discovered every day. In the subject of biology, classification is extremely important. So the organisms are classified based on the two qualities, and these features are used to classify the organisms. The term dichotomous refers to something that is divided into two pieces.
Using a dichotomous key series#
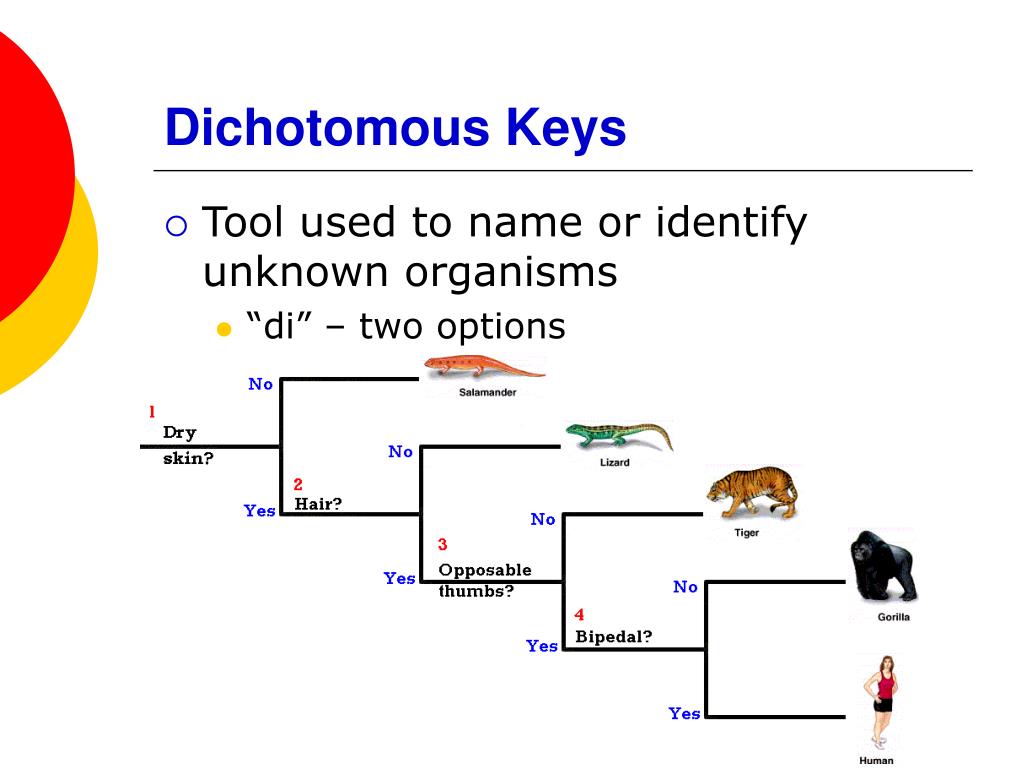
Dichotomous keys are made up of a series of statements, each with two options, that guide users to the proper identification. The keys in Wikibooks are still under development.Hint: A dichotomous key is a useful scientific tool for identifying various organisms based on their observable characteristics.
Chimaera: Upper jaws are fused with skull has separate anal and urogenital openings Only three pairs of large, permanent grinding tooth plates Has a gill covering similar to that of bony fishes.Shark: Upper jaws not fused to skull Has only one anal/urogenital opening Has many sharp, replaceable teeth Gill covering absent.What kind of fish is it? (Osteichthyes): Actinopterygii & Sarcopterygii, but also lampreys (Myxini) and hagfish (Petromyzontida) Scorpion (Scorpiones), also Palpigradi, Amblypygi, Solifugae, Thelyphonida, Schizomida, and maybe Pseudoscorpionida just in case.Shrimp (Dendrobranchiata & Caridea), also Cumacea, Stomatopoda, and Stenopodidea (just in case).Lobster or Crayfish (Astacidea) also achelata.Crab (Brachyura) also anomural (hermit crabs).If the description and other information satisfactorily confer, then a correct identification is possible.ĭoes it live underwater or mostly underwater? The habitat and location where the sample was collected is useful for plants.
Using a dichotomous key verification#
Finally, a verification step is important by comparing the specimen with any further details available including description,photographs and other reference. If the description at each level does not appear accurate then back up to some earlier couplet and start over, questioning each decision more carefully. Organism is identified as much as possible.Use choices given to arrive at the lowest possible level.Archaea - Relatively small group of single-celled prokaryotes more closely related to the eukaryotes than to the bacteria.Bacteria - Ubiquitous, single-celled prokaryotes a few microns in size, with varying morphology.Like plants, they are sessile, but unlike plants they lack chloroplasts and are heterotrophic (with exceptions). Typically eukaryotic, multicellular organisms. Protista - (A contested group of around 40 phyla of eukaryotic organisms) Typically simple, eukaryotic unicellular microorganisms or multicellular microorganisms without specialized tissues.They lack rigid cell walls and are heterotrophic (with exceptions). Typically multicellilar, motile organisms.
They are autotrophs, and photosynthesize (with exceptions). Their cells have walls composed of cellulose.

Typically multicellular, sessile organisms. Keys usually start with a first selection from the following: Taxonomic systems vary, but the following system has been found useful: The systems attempt to model the natural order, thus helping research by classifying different organisms. Taxonomic systems are based on similar characteristics or increasingly on DNA analysis. This key uses hyperlinks to navigate.Ĭlassification with keys On selecting one, the reader is presented with the next couplet choice in the key and so on - to eventually arrive at an identification. For example, 'it is either red or it isn't'. The statements should be mutually exclusive for the key to work efficiently. For convenience, there may be polytomous sections within the book.Ī written dichotomous key presents the reader with two statements that describe certain characteristics. The method adopted uses mostly a dichotomous key based on two choices, which is either in written format or pictographic, or both. This e-book can help with the identification of unknown organisms or species.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
